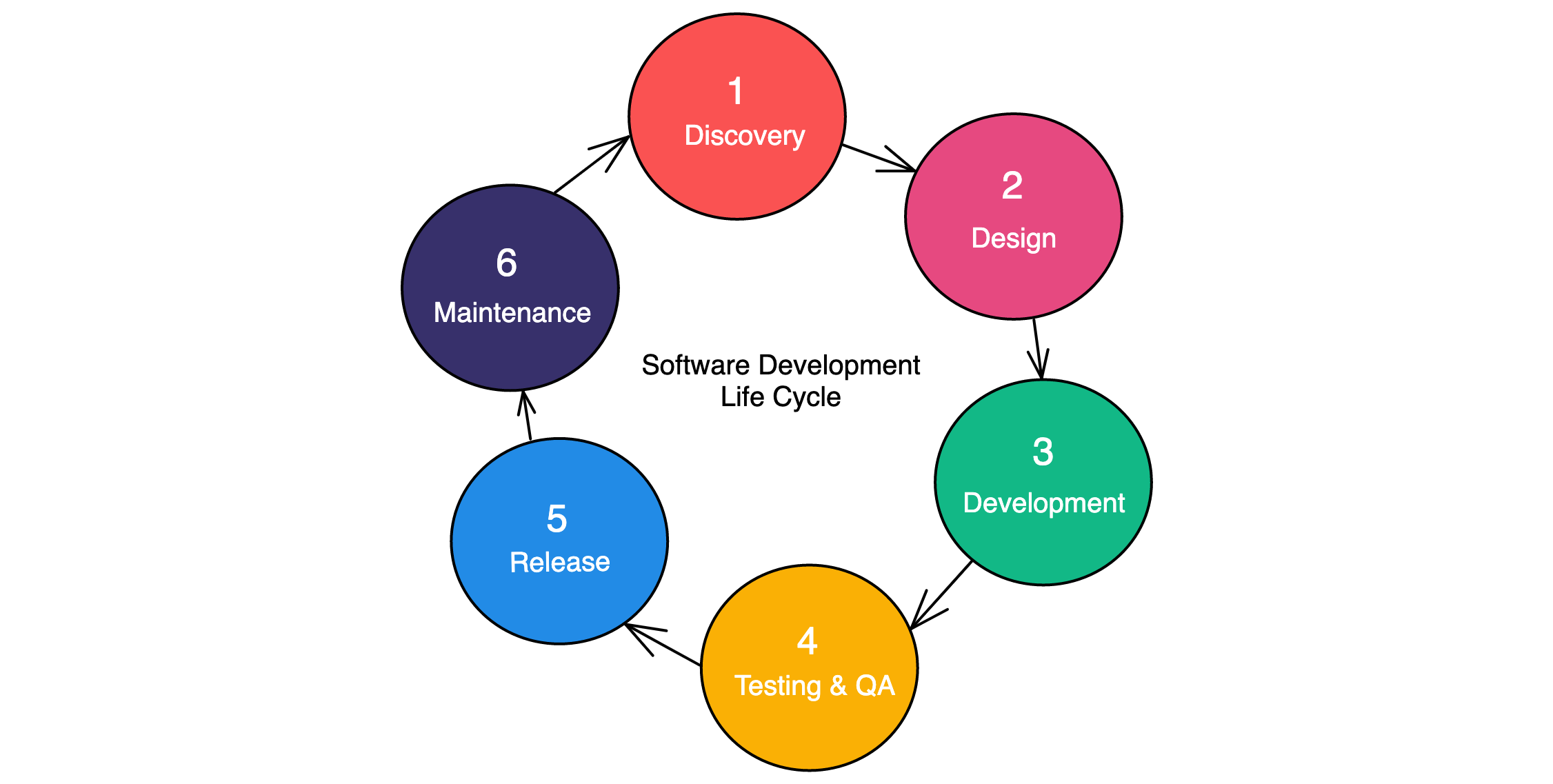
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process used to design, develop, and deliver software products efficiently. It involves planning, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance stages.
The SDLC framework helps teams organize and manage the software development process effectively. By following a structured approach, companies can ensure the quality, timely delivery, and cost-effectiveness of their software products. Embracing SDLC best practices leads to improved collaboration, minimized risks, and enhanced overall project success.
It is a crucial methodology for creating high-performing and reliable software solutions that meet customer requirements and industry standards.
Credit: www.couchbase.com
Introduction To Software Development Life Cycle
Discover the Software Development Life Cycle, a structured approach to software development process management. It encompasses planning, design, development, testing, deployment, and maintenance phases to ensure successful project execution. This systematic framework enhances efficiency and product quality.
The Essence Of Sdlc
Software Development Life Cycle or SDLC is the process of developing software applications that are efficient, effective, and reliable. This process involves a series of steps that start from planning and end with maintenance. The SDLC model is a framework that ensures that the software development team follows a structured approach to produce software that meets the client’s needs.Key Benefits For Businesses
The benefits of implementing SDLC are not only limited to software development teams but also extend to businesses. Here are some of the key benefits that businesses can enjoy by adopting SDLC:- Efficient Project Management: SDLC ensures that the project is properly planned, executed, and controlled. This leads to better project management and reduces the risk of project failure.
- Improved Quality: SDLC ensures that the software meets the client’s needs and is of high quality. This leads to customer satisfaction and reduces the number of defects and bugs in the software.
- Cost Savings: SDLC ensures that the software development process is streamlined and optimized. This leads to cost savings for businesses as it reduces the development time and the number of defects in the software.
- Increased Productivity: SDLC ensures that the software development team follows a structured approach and is more productive. This leads to faster development times and better quality software.
Different Models Of Sdlc
Explore various SDLC models like Waterfall, Agile, and DevOps, each offering unique approaches to software development processes. These models guide teams through planning, development, testing, and deployment stages, ensuring efficient project management and quality deliverables.
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a process of developing software from conception to retirement. It is essential to follow the right model of SDLC to ensure the success of software development. Different models of SDLC have been designed to meet the varying demands of software development projects. In this blog post, we will discuss some of the popular models of SDLC, including the Waterfall Model, Agile Methodology, Spiral Approach, and DevOps Integration.Waterfall Model
The Waterfall Model is a traditional approach to software development. It is a linear, sequential model consisting of distinct phases that must be completed in order before moving on to the next phase. The phases of the Waterfall Model include requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, deployment, and maintenance. This model is best suited for projects that have well-defined requirements and where changes are unlikely to occur during the development process.Agile Methodology
Agile Methodology is a flexible, iterative approach to software development. It is an alternative to the Waterfall Model and emphasizes collaboration, continuous feedback, and rapid prototyping. Agile projects are divided into small iterations, and each iteration includes planning, design, development, testing, and review. Agile is best suited for projects with dynamic requirements and where changes are expected during the development process.Spiral Approach
The Spiral Approach is a risk-driven model that combines the elements of both the Waterfall Model and Agile Methodology. It is an iterative model that emphasizes risk analysis, prototyping, and continuous evaluation. The Spiral Approach consists of four phases: planning, risk analysis, engineering, and evaluation. This model is best suited for large and complex projects with high risks.Devops Integration
DevOps Integration is a relatively new model of SDLC that emphasizes collaboration between development and operations teams. It is an approach that combines the best practices of software development and IT operations to deliver software faster and with higher quality. DevOps Integration involves continuous integration, continuous delivery, and continuous testing. This model is best suited for organizations that want to improve the speed and quality of software delivery while reducing costs and risks. In conclusion, choosing the right model of SDLC is critical to the success of any software development project. Each model has its advantages and disadvantages, and it is essential to select the model that best meets the project’s requirements. By considering the Waterfall Model, Agile Methodology, Spiral Approach, and DevOps Integration, you can choose the right model of SDLC that aligns with your project goals and objectives.Phases Of Sdlc
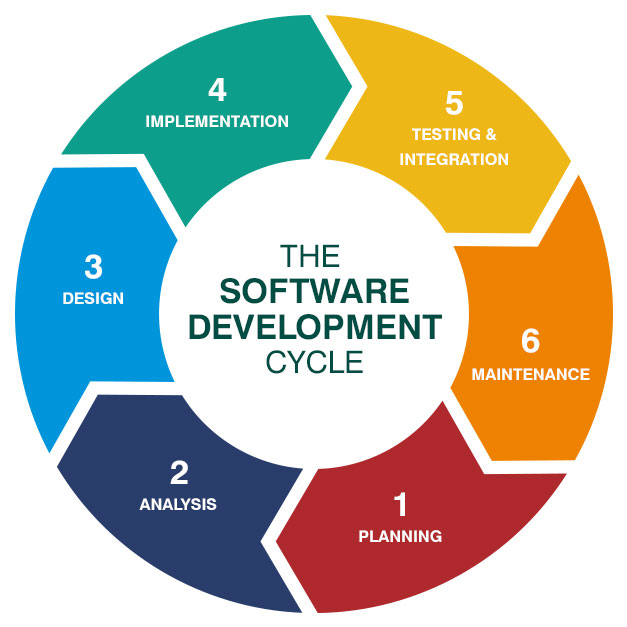
Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is a systematic approach to develop software applications. It consists of several phases that ensure the smooth and efficient development of software. Each phase has its own objectives and activities, which contribute to the overall success of the project. Let’s explore the different phases of SDLC:
Requirement Analysis
During this phase, the development team gathers information about the software requirements from the stakeholders. They analyze and document these requirements, ensuring a clear understanding of the project goals and user needs. This helps in creating a solid foundation for the subsequent phases.
Design And Prototyping
Based on the requirements gathered, the team moves on to design the software architecture and user interface. This phase involves creating detailed system and database designs, as well as developing prototypes to validate the design concepts. It aims to ensure that the software meets the functional and aesthetic expectations of the users.
Software Development
Once the design is finalized, the actual coding and programming of the software begin. The development team follows the best practices and coding standards to write clean and efficient code. This phase involves continuous collaboration between developers, ensuring the smooth implementation of the design specifications.
Testing
Testing is a crucial phase of SDLC, where the software is thoroughly checked for any defects or bugs. The testing team creates test cases and scenarios to validate the functionality and performance of the software. They identify and report any issues, which are then fixed by the development team. This phase ensures the delivery of a high-quality and reliable software product.
Deployment
Once the software passes the testing phase, it is ready for deployment. The development team installs and configures the software in the target environment, ensuring its compatibility and smooth operation. This phase involves proper documentation and user training to facilitate a seamless transition to the new software system.
Maintenance And Updates
After the software is deployed, it enters the maintenance phase. This phase involves ongoing support, bug fixes, and updates to ensure the software remains functional and up-to-date. Regular maintenance activities, such as performance optimization and security enhancements, help in maintaining the software’s efficiency and reliability.
In conclusion, the phases of SDLC, including Requirement Analysis, Design and Prototyping, Software Development, Testing, Deployment, and Maintenance and Updates, work together to ensure the successful development and implementation of software applications. Each phase plays a vital role in delivering high-quality, user-friendly, and reliable software solutions.
Choosing The Right Sdlc Model
When it comes to software development, choosing the right Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) model is crucial for the success of the project. The SDLC model defines the stages and processes involved in software development, and selecting the most appropriate model depends on various factors such as project size and complexity, stakeholder involvement, risk assessment, and time to market.
Project Size And Complexity
The size and complexity of a project play a vital role in determining the most suitable SDLC model. For small projects with clear and well-defined requirements, an agile or iterative model may be more appropriate. On the other hand, large-scale projects with complex requirements may benefit from a more structured and sequential approach, such as the waterfall model.
Stakeholder Involvement
Stakeholder involvement is another key consideration when selecting an SDLC model. In projects where stakeholders are actively engaged and provide continuous feedback, an agile or iterative model that allows for frequent collaboration and adjustments may be the best fit. Conversely, in projects with minimal stakeholder involvement, a more rigid and linear model like the waterfall approach may be suitable.
Risk Assessment
Assessing and managing risks is essential in software development. For projects with high uncertainty and evolving requirements, an adaptive SDLC model like the spiral model or agile methodologies can help mitigate risks through iterative development and frequent reassessment. Conversely, projects with well-defined and stable requirements may opt for a more predictive model like the waterfall or V-shaped model.
Time To Market
The time to market is a critical factor in today’s fast-paced business environment. Projects requiring rapid deployment and frequent releases may benefit from agile or iterative models, allowing for incremental development and quicker delivery of features. Conversely, projects with longer development timelines and a focus on comprehensive planning may align better with the waterfall or V-shaped model.
Tools That Facilitate Sdlc
When it comes to software development, having the right tools in place is crucial for a smooth and efficient Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC). These tools help streamline various processes and improve collaboration among team members. In this section, we will explore some of the essential tools that facilitate SDLC.
Project Management Software
Project management software plays a vital role in keeping the development process organized and on track. It enables teams to plan, track, and manage tasks, deadlines, and resources effectively. With features like task assignment, progress tracking, and communication tools, project management software ensures that everyone is on the same page and aware of their responsibilities.
Version Control Systems
Version control systems are essential tools for managing source code and tracking changes made by multiple developers. These systems allow team members to collaborate seamlessly on a codebase, maintaining a history of modifications and enabling easy identification and resolution of conflicts. Popular version control systems like Git provide a centralized repository to store code and facilitate efficient collaboration.
Continuous Integration Tools
Continuous Integration (CI) tools automate the process of integrating code changes into a shared repository, ensuring that builds are always up to date and functional. These tools enable developers to detect integration issues early on, improving code quality and reducing the risk of bugs in the final product. CI tools like Jenkins and Travis CI automate the build and testing processes, making them an integral part of the SDLC.
Testing Frameworks
Testing frameworks are essential for ensuring the quality and reliability of software. These frameworks provide a structured approach to testing, allowing developers to write test cases, execute them, and report any failures or issues. By automating the testing process, these tools save time and effort, enabling developers to identify and fix bugs efficiently. Popular testing frameworks include Selenium for web applications and JUnit for Java-based projects.
In conclusion, having the right tools in place is crucial for a successful SDLC. Project management software, version control systems, continuous integration tools, and testing frameworks are just a few examples of the tools that facilitate the various stages of the development process. By leveraging these tools, development teams can improve collaboration, ensure code quality, and deliver high-quality software products.

Credit: www.geeksforgeeks.org
Role Of Documentation In Sdlc
The role of documentation in the Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) is crucial for the success of any software project. Documentation serves as a detailed record of the project’s requirements, design, implementation, and testing phases. It helps in maintaining consistency, transparency, and traceability throughout the SDLC process.
Creating Effective Documentation
Effective documentation is clear, concise, and comprehensive. It should be formatted in a structured manner, making it easy to navigate and understand. Incorporating diagrams, flowcharts, and examples can enhance the clarity of the documentation.
Documentation For Different Phases
Documentation is essential for each phase of the SDLC. During the requirements phase, it includes business requirements, functional specifications, and use cases. In the design phase, it encompasses system architecture, database design, and interface specifications. The implementation phase documentation comprises code comments, test cases, and user manuals. Finally, the testing phase involves test plans, test cases, and defect reports.
Maintaining Documentation Integrity
Maintaining the integrity of documentation involves regular updates and version control. It ensures that the documentation remains accurate and reflects the current state of the software project. Implementing a robust change management process is crucial to maintaining the integrity of documentation throughout the SDLC.
Challenges In The Software Development Process
The Software Development Life Cycle presents numerous challenges, including managing changing requirements, ensuring thorough testing, and maintaining communication among team members. These obstacles demand careful planning and execution at each stage to deliver a successful software product.
Managing Changing Requirements
Software projects often face difficulties in managing evolving requirements.
Requirements changes can impact timelines and resources.
- Regular communication is crucial for adapting to changes.
- Implementing agile practices helps in flexibility.
Ensuring Quality And Security
Quality and security are paramount challenges in software development.
Quality assurance processes are essential for bug detection.
- Security measures must be integrated throughout the lifecycle.
- Regular testing helps in identifying vulnerabilities.
Dealing With Technical Debt
Accumulated technical debt poses a significant challenge in development.
Addressing technical debt prevents future complications.
- Regular code refactoring minimizes technical debt.
- Investing time in maintenance reduces long-term issues.
Future Trends In Sdlc
In the future, Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning will play a crucial role in enhancing the Software Development Life Cycle.
The increasing demand for DevSecOps reflects a shift towards more secure and collaborative software development processes.
Embracing a product mindset over a project mindset ensures continuous improvement and customer-centric development.
Credit: bigwater.consulting
Conclusion
Understanding the software development life cycle is crucial for successful project management. By following the phases of planning, development, testing, and deployment, businesses can ensure efficient and effective software delivery. Embracing this structured approach can lead to improved quality, reduced costs, and enhanced customer satisfaction.
